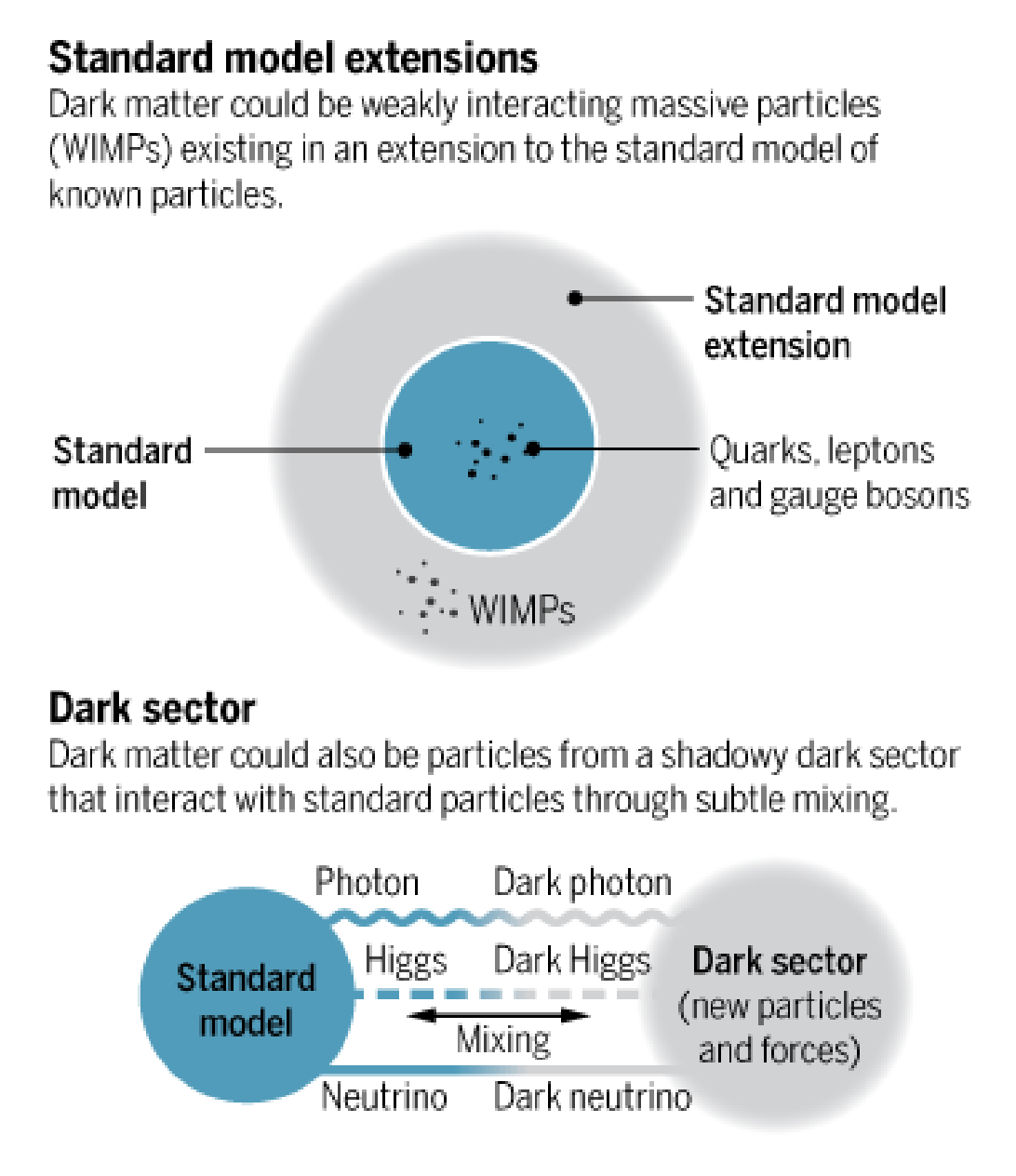
Dark Sector Searches in ATLAS
Edinburgh’s work on ATLAS includes searches for exotic particles predicted in extensions of the Standard Model (SM). Some of these extensions propose a new dark sector of particles that mix subtly with SM particles and where Dark Matter (DM) candidates appear. In this scenario, new dark mediators (e.g., a new dark photon) can be massive and long-lived while decaying to SM particles and leaving leave distinguishable signatures in the detector. These dark photon decays would produce collimated decay products in a jet-like structure that receive the name of Dark Photon Jets (DPJ).
At Edinburgh, current efforts aim to study the expected sensitivity to these objects coming from decays of the Higgs boson. In particular, special interest is payed to events where the Higgs was produced via the Vector Boson Fusion (VBF) mechanism, in order to exploit its well known signature to increase the sensitivity of the search.